Let’s Dive into UEFI Firmware Development with EDK2 Together!
Welcome to SecureMyByte! If you’re here, you probably love tinkering with firmware as much as I do.
Or maybe you’re just looking to make your computer boot faster so you can get to your cat videos quicker.
Either way, you’re in the right place!
Why Bother with UEFI Firmware?
- Enhanced Security: Because who doesn’t want their firmware to be a bouncer that only lets the good bits in?
- Faster Boot Times: Less time waiting, more time doing… well, anything else!
- Modern Features: Support for ginormous hard drives, fancy graphical interfaces, and even networking during boot – because why not?
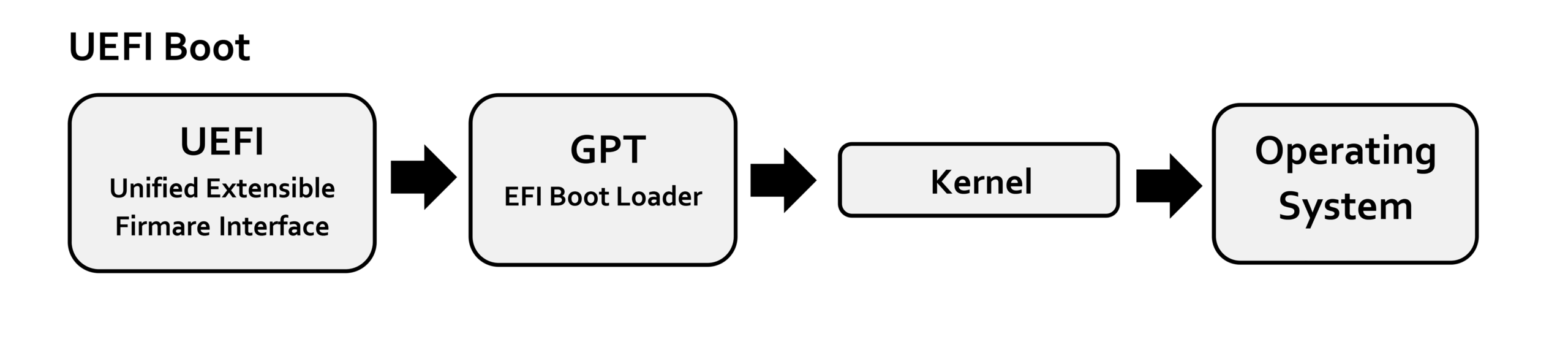
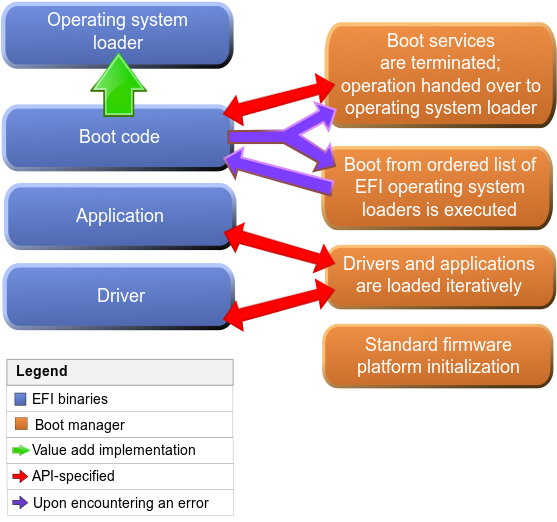
What the Heck is EDK2?
EDK2 (EDK II) is like the Swiss Army knife of UEFI firmware development. It’s open-source, it’s powerful, and it’s here to make your life easier. And I’m here to guide you through it – step-by-step, like a firmware Sherpa.
Our (Mis)Adventures in UEFI Firmware
Blog Series
- Getting Started with EDK2 – Because everyone needs a good starting point.
- Setting Up Your Development Environment – The feng shui of coding.
- Creating Your First UEFI Application – Your very first “Hello, Firmware!”.
- Advanced UEFI Programming – For when you’re ready to level up.
- Debugging and Troubleshooting – Or as I like to call it, “Where did I go wrong?”
- Practical Applications of UEFI Firmware – Real-world wizardry.
Video Tutorials
- Introduction to UEFI and EDK2 – We meet face-to-face, sort of.
- Setting Up Your Development Environment – Let’s get you all set up!
- Writing Your First UEFI Application – Time to roll up those sleeves.
- Exploring UEFI Protocols – Diving deeper together.
- Advanced UEFI Programming Techniques – Showing off some pro moves.
- Debugging UEFI Applications – Fixing stuff, one bug at a time.
- Real-world Applications and Future Trends – Because the future is now.
Unlocking User Data Security: Accessing Data Without Booting into Windows
At SecureMyByte, I’ll show you how to access user data stealthily, bypassing Windows OS entirely.
Security Considerations: Accessing drives this way can bypass OS-level security, so proceed cautiously.
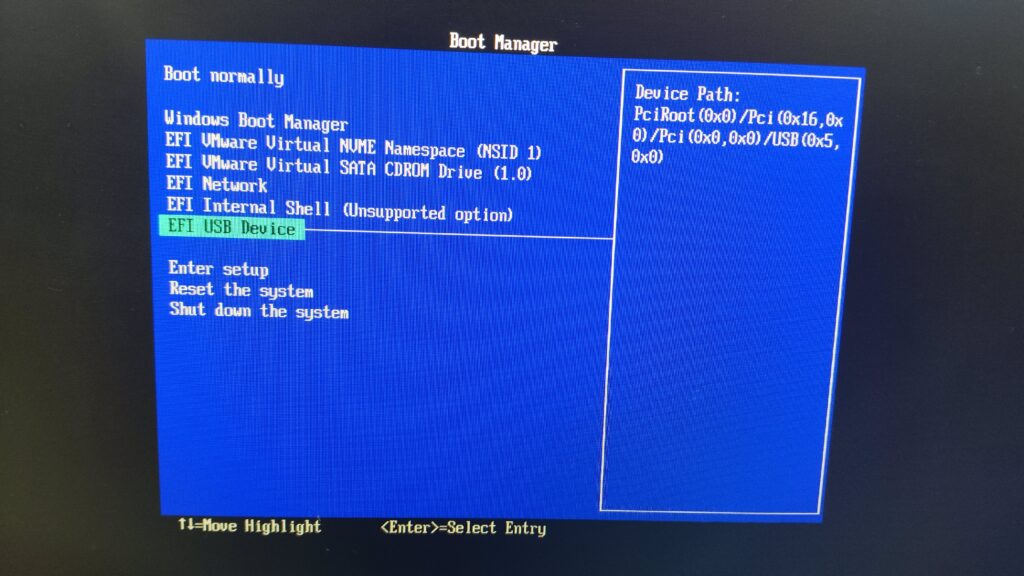
Reverse Shells in UEFI with Python
𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐅𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐬:
𝐑𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐭𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐄𝐱𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧: Connect to a specified server and port to receive and execute commands on the local machine.
𝐔𝐄𝐅𝐈 𝐒𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐨𝐥: Manage and execute commands on UEFI systems remotely.
𝐒𝐨𝐜𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧: Establish a secure connection to receive commands and send back the output.
FTP Client in UEFI with Python
𝐊𝐞𝐲 𝐅𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞𝐬:
𝐑𝐞𝐦𝐨𝐭𝐞 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐦𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐄𝐱𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧: Connect to a specified server and port to receive and send files on the local machine.
𝐔𝐄𝐅𝐈 𝐒𝐲𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐦 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐨𝐥: Manage and File on UEFI systems remotely.
𝐒𝐨𝐜𝐤𝐞𝐭 𝐂𝐨𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧: Establish a secure connection to receive file and send back.
